Indo-Nepal trade relation is governed by the bilateral treaties of trade and transit & agreement for co-operation to control unauthorized trade signed in the year 1971,1978,1996,2002,2009 respectively. Indo-Nepal trade treaty which took in 1996 was a land mark breakthrough in Indo-Nepal bilateral trade. Under this agreement India provided duty free across to all products which were manufacture in Nepal on the basis of a certificate of origin issued by the Nepali authorities with no minimum requirement of domestic value addition. Under the agreement noval added criteria were needed for products manufactured in Nepal to qualify for tariff concession on entry in Indian market. As a request of this Nepali’s trade with India thrive because it was benefited by the 1) low duty rate that had imposed on raw material imported compare to prevailing tariff rate on raw materials in India and 2) tariff figure offer on all products which were imported from Nepal by India under the provision of Indo-Nepal trade agreement.
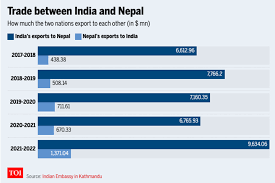
Another important agreement are the treaty of trade and the agreement of co-operation which were signed between the two countries on 27th October 209 at (Kathmandu) Nepal. The treaty aims at improving bilateral trade between the two countries by increasing the mutually agreed point of trade. An Inter government committee (IGC) member on matters f trade, transit and co-operation to control Unauthorized and illegal trade was held in December. Both side had detailed discussion on various bilateral issues. Nepalese request for waiver of additional customs (ADC) on all export items to India was also considered. Provision of treaty of trade signed in October for replacement of duty refund procedure (DRP) has been implemented. Double taxation avoidance agreement (DTAA) with Nepal was signed on 27th November to help exporters and inventors of both countries in improving mutual business engagement. India’s trade with has increased substantially from US $ 1233.42 Million in 2006-07 to US $ 3634.94 Million in 2012-13. There are five state in India which touches Nepal boundaries namely WB, UP, UK, SIKKIM, BIHAR at India Nepal border. The GOM recommended setting up immigration check post (IMCPS) and land custom station, in order to check the illegal movement of people and goods.
Including point and ICD between two countries :- Twenty two land border points have been specified as agreed routes for India-Nepal bilateral trade and for India- Nepal transit.
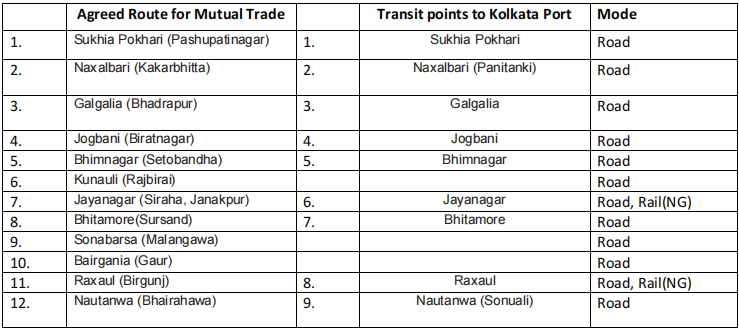
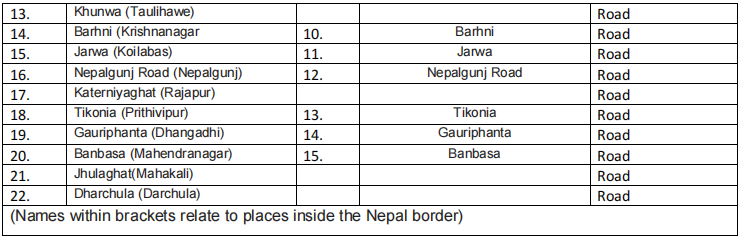
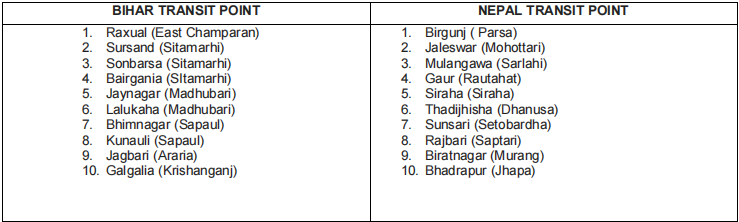
Out of these 22 specified routes, the bulk if interchange takes place through 5 routes namely 1) Raxaul (Birgunj) 2)Jogbani (Biratnagar), 3) Nautanwa (Bhairahawa), 4) Naxalbari (Kakarbhitta), 5) Nepalgunj Road (Nepalgunj). Container freight station have been provided in Birgunj, Biratnagar and Bhairahawa in Nepal. Among them, only Birganj in rail linked by Indian railways broad-gauge railway system Raxaul (Birgunj) is the most import route for bilateral trade between India and Nepal and its trade without other countries. Further, Birgunj is the only rail linked dry port (sirsiya dry port) in Nepal with an inland container clearance deport equipped to handle both break bulk and containerized cargo. There well designed ICD have been opened. The rail ICD at Birgunj and road ICD at Bhairahawa and Biratnagar a fourth ICD is planned at Kakarbhitta. The ICD were established to handle third country transit traffic but now also handle bilateral trade. Out of this only Birgunj ICD is capable to handle cargos by the both rails and trucks. State wise Indo-Nepal transit point Bihar shares a large part of its border with Nepal, including 10 transit point for Indo-Nepal trade. There is much potential for economic gains towards which India and the state of Bihar Co-operative with Nepal within the mutually agreed formal frame work. The region has location advantage that bestows natural Interdependence which is yet to be utilized. There is a need to shift from bilateralism to sub regionalism as far as South Asian regional co-operation is concerned of all the transits in Bihar, Raxual and Jogbani, falling in the districts of East champaren and Araria, respectively account for the majority if Indo-Nepal trade through bihar. In fact, Raxual and Jogbani are among the five most import transit route between India-Nepal along with Nautanwa and Nepalganj in U.P and Naxalbari in W.B. Raxual-Birganj route is most bilateral trade between India-Nepal as well as for Nepal’s trade with third country
Nepal border touches in West Bengal: ICP Panitanki is located in the state of West Bengal of Darjeeling District along the international border India and Nepal.
ICP Panitanki lies in close proximity of NH 327 and well connected with Asian Highway (AH-2). In term of rail connectivity, it is located 4km from Batasi Railway Station. There is also Proposed Trans-Asian Railway connectivity at Panitanki. The Status as September 2021 is that LPAI has prepared detailed project and has identified 38.30 acres of land for development of the ICP. The State Govt. of West Bengal has been requested for initiating the process of land acquisition the major commodities via Panitanki LCS are Coal, Petroleum
Products, Raw Jute, Cycle and Cycle Parts, Cement Clinker/ Slag, and Vegetables and major commodities of Import are tea, ginger, noodles, Plywood.
Trade Point at Sunauli In Uttar Pradesh: Sunauli is a popular transit point between Nepal and India, Which is also known as the trade point lies 70 km north of Gorakhpur and 3 km South of Bhairahawa, While the Indian side is called “Sunauli” the Nepal side is known as Belahiya. Belahiya – Sunauli is about 5 – 10 minutes away from Bhairahawa. Sunauli gives an excellent glance of the local life style of both of nation.
Uttarakhand – Banbasa is a census town in champawat district in the state of Uttarakhand. India most famous for its border crossing into Nepal from India.
Furthermore, the possibilities of cross- border trade between North East India-Nepal is very low as out of all North Eastern Indian States, Only Sikkim shares its international Border 978km with Nepal. In addition to it North Sikkim is the least populated, situated at high elevation and covered with Himalaya mountains. The only area that covered as a potential zone for trade cross border trade between two regions is Western Sikkim, Which lies above Singalia National park at Darjeeling. North East Region does not contribute any significant amount in trade between India and Nepal as most of the trade between two countries. The share of Nepal in total North East Indian trade with its Neighboring countries is merely 0.30 % in 2016-17.
Principal Export to Nepal: Mineral fuels, Mineral oil, Products of their distillation, Bituminous substance, Vehicles other than railway or tramway rolling stock, Pharmaceutical products, cereals, Iron and Steel, cotton, plastic, Electrical machinery.
Principal Import from Nepal: Iron & steel, animal or vegetable fat and oil, plastic, manmade staple fibers, cop reel, Tea, mate, spices, beverages, cosmetics.